| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Philosophical Importance of Water |
As Thales stated, "Water is the origin of all things," water is fundamental for sustaining life and civilization. |
| Water Cycle | Sun heat → Evaporation (ocean, surface) → Clouds/fog → Precipitation (rain, snow) → Surface water → Infiltration to ground/return to sea → Re-evaporation; a complex circulation process. |
| Water Utilization | Rivers, lakes, and groundwater are used for drinking water, agriculture, industry, and power generation. |
| Water and Civilization | Interruption of water supply significantly impacts cultural life; long-term disruption threatens survival. |
| Situation in Korea | Since the 1960s, industrialization, urbanization, and population growth have sharply increased water demand, prompting water resource development and expansion of water supply facilities. |
| Current Issues | Quantity: Transition from seemingly infinite to finite resources Quality: Increase in wastewater and pollution Rising demand for clean water among the public |
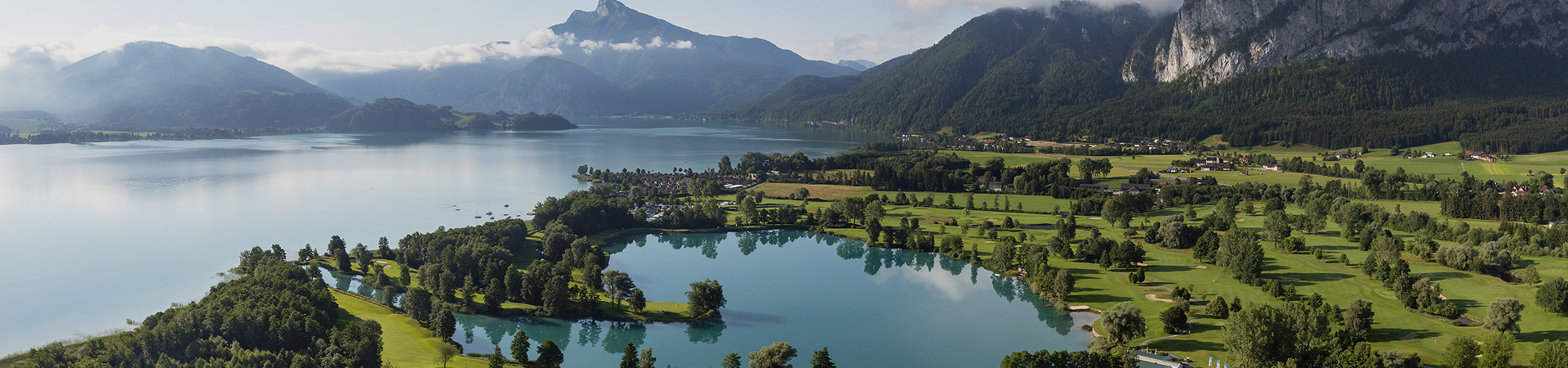
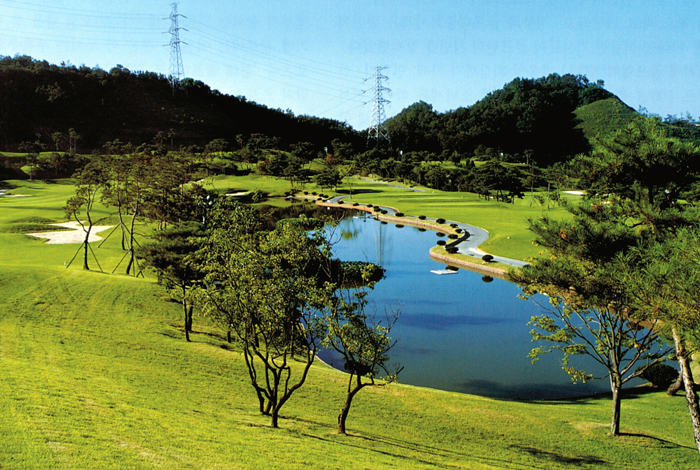
| Environmental Functions of Water |
Landscape and aesthetic functions (harmonization with greenery) Water source and discharge functions Environmental preservation roles (retention of residual pesticides, fertilizers, etc.) |
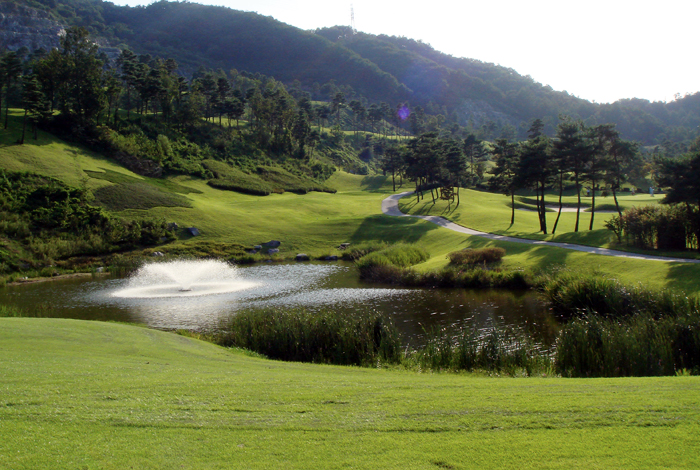
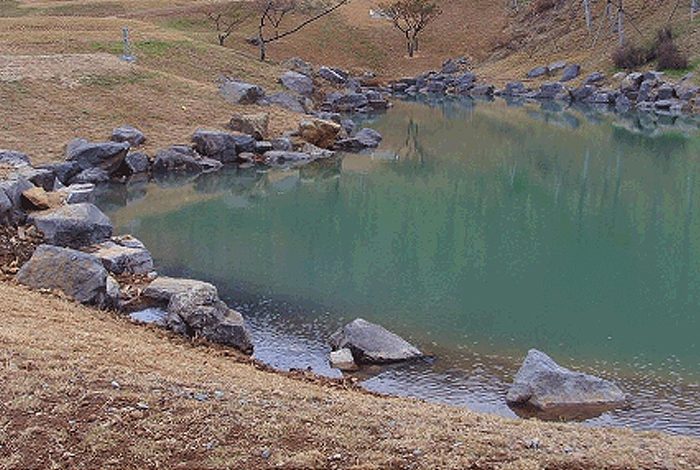
| Golf Course Pond Examples |
Landscape and aesthetic functions Strategic play functions Water storage and drainage functions Environmental preservation functions |
| Water Resource Strategy Directions |
Consider difficulty of new development Ensure efficient management Minimize waste Maximize use of existing facilities Long-term strategy considering future generations |

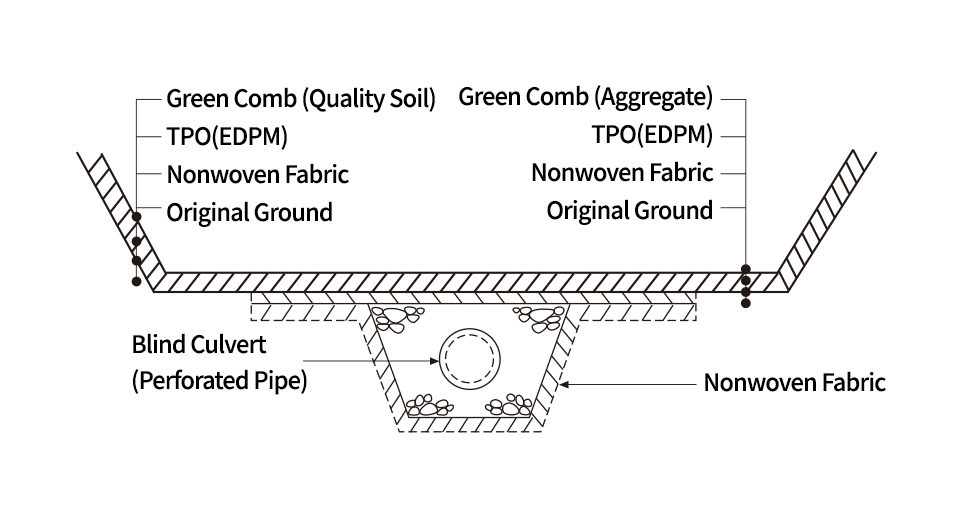
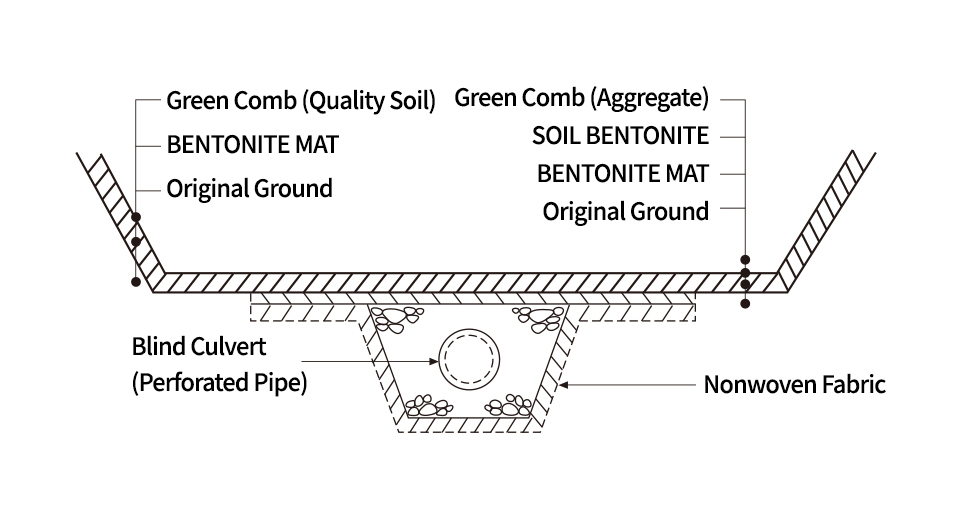
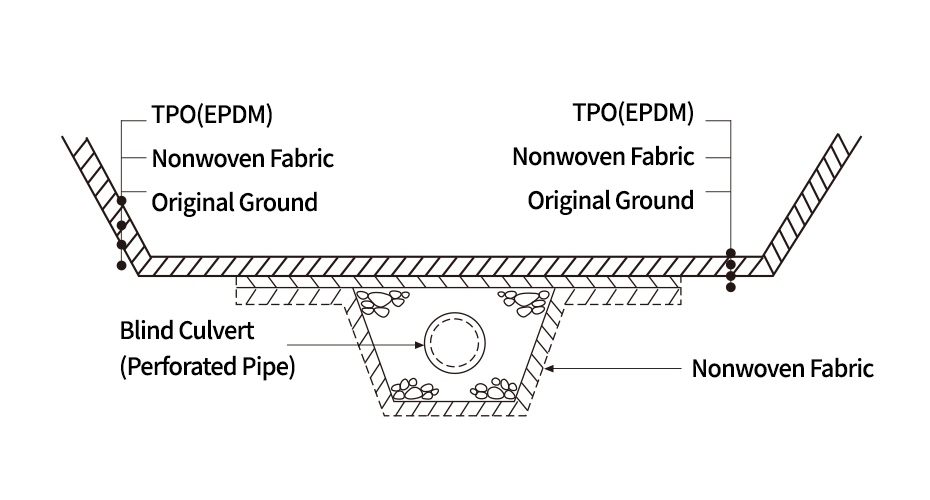
TPO (EPDM) Sheet, Bentonite Mat, Soil Bentonite, Geocomposite



| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Outer edge of the hole, green, or bunker |
| Main Functions | Provides space for aquatic plants, responds to water level changes during dry seasons, accommodates H.W.L (high water level) fluctuations |
| Design & Construction Features |
Creates visual aesthetics while maintaining ecological functions |
| Materials Used | Timber, cobblestones, natural stones, turf, and other environmentally friendly materials |

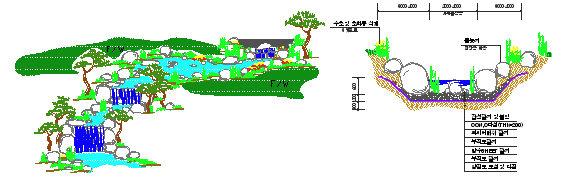
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A small canal used for drainage, irrigation, or circulation |
| Construction Method | Created by modifying natural valleys into golf course features, or artificially formed using terrain variations |
| Feature | Often includes waterfalls |
| Location | CREEK connects from the highest artificial pond to the lowest pond on the golf course |
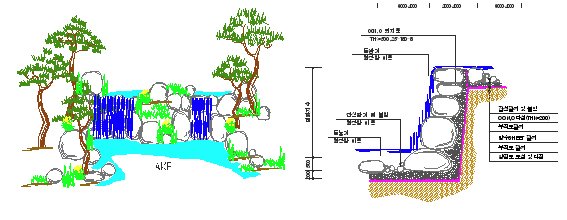
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Water flows nearly vertically, forming a waterfall over slopes or steps using height differences |
| Function | Provides aesthetic appeal |
| Installation Elements | Design and appearance vary depending on location, materials, height, and water drop |
| Types | Ranges from large to small scale; maintaining a natural landscape is important |
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
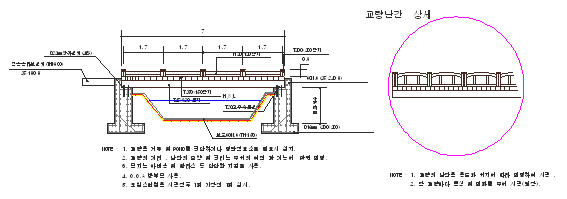
| Definition | Elevated structures crossing rivers, lakes, straits, bays, canals, lowlands, or other facilities (bridges) |
| Function | Ensures safe passage and facility stability |
| Requirements | Sufficient strength and durability, cost-effectiveness, and structural design for stability and usability |
| Design Considerations | Material selection, structural type comparison, and aesthetic integration with the environment |