

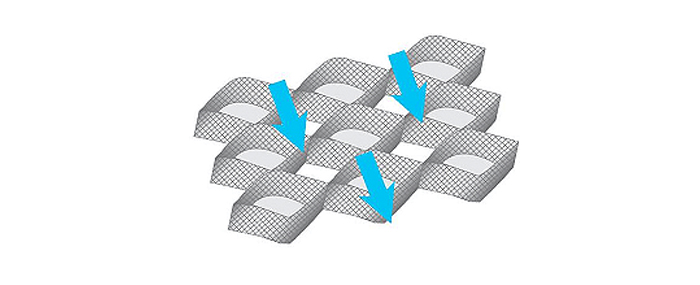
When the infill material is confined within the cells, the cell walls act
as surrounding walls encasing the soil mass, and the adjacent cells
provide horizontal stress support, keeping the cell walls in a neutral
position and maintaining their self-supporting property.
Filled Greencomb behaves like a slab, distributing loads and
restraining vertical displacement, thereby enhancing ground bearing capacity.
Using porous lattice strips,
water can flow freely between cell walls, making it easy to apply
as a drainage layer with infill materials such as aggregates.
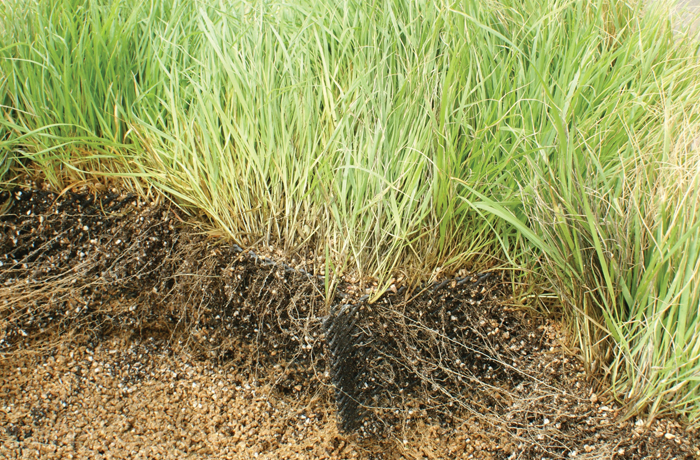
When applied as a vegetative base layer, roots penetrate the perforations
of the porous strips, anchoring the plants and integrating them
with the structure, which increases the overall system stability.

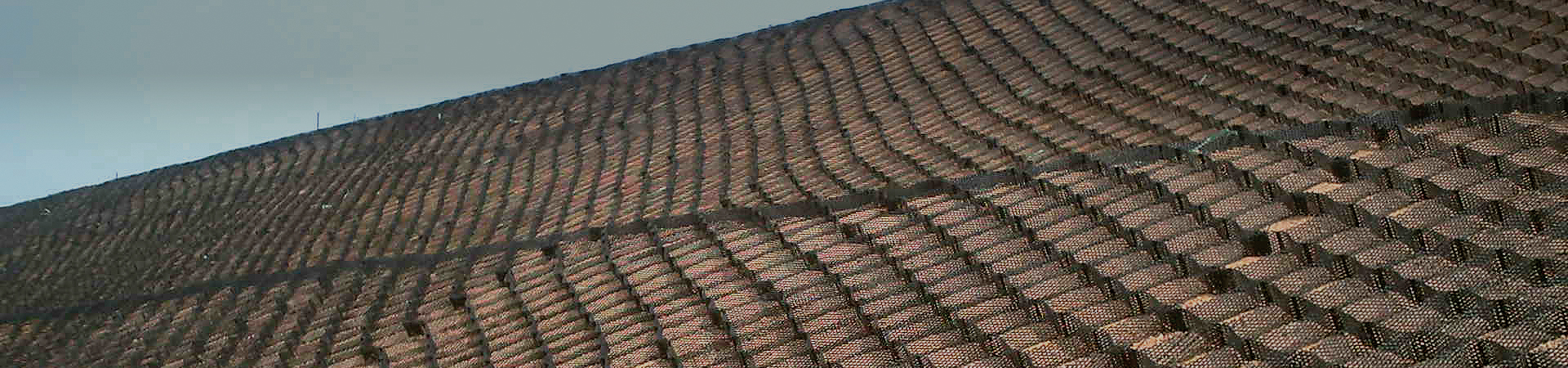
The lattice cell wall structure provides friction with the infill material
that is superior to conventional smooth-sheet geocells,
enhancing the confinement effect of the soil particles.
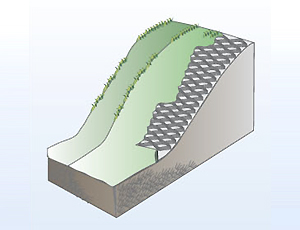
Provides stable slope reinforcement by ensuring
excellent friction with soil. Constrains soil
particles to resist erosion caused by heavy
rainfall effectively.
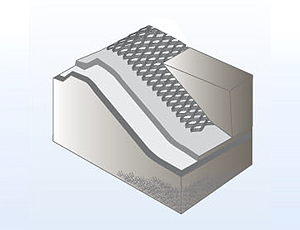
Provides excellent drainage and protective
capabilities, replacing conventional petaire
drainage/reinforcement layers.
Forms a relatively thin drainage layer,
maximizing landfill space utilization.
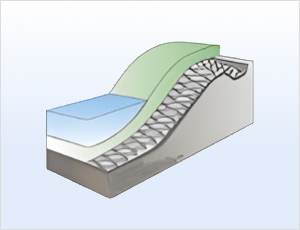
Forms eco-friendly vegetative waterways with
excellent permeability, providing stable
performance under various hydraulic conditions.
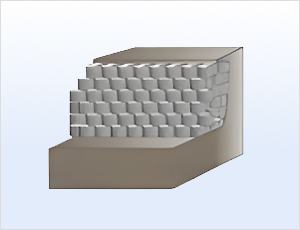
Minimizes deformation by constraining soil
particles, forming a stable earth mass
suitable for reinforced or gravity
retaining walls.
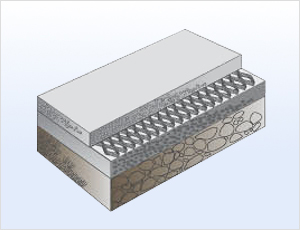
Strengthens the sub-base to prevent differential
settlement and improve support using
the Greencomb method.
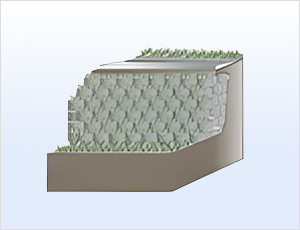
Encourages vegetation on the Greencomb
surface to form an eco-friendly soil structure.
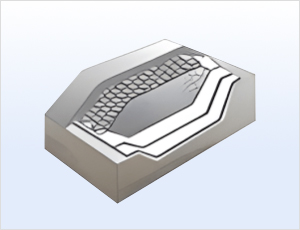
An efficient method to prevent erosion and
differential settlement of the vegetative
base layer on the final landfill cover.
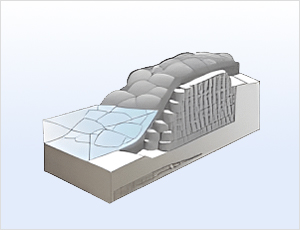
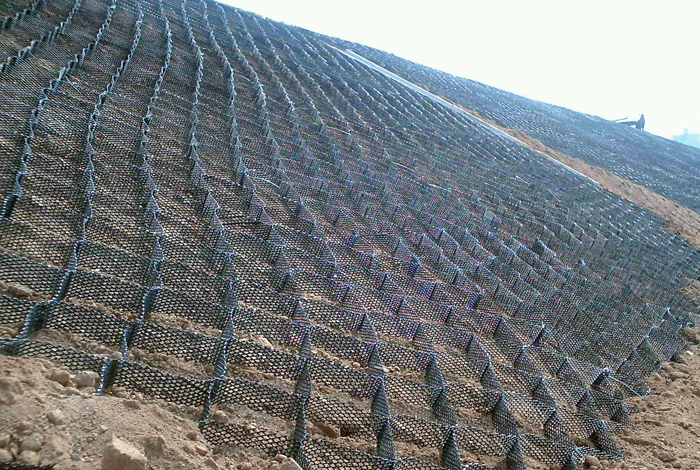
Allows manual construction during emergencies.
Simple and quick installation makes it ideal
for urgent riverbank restoration works.

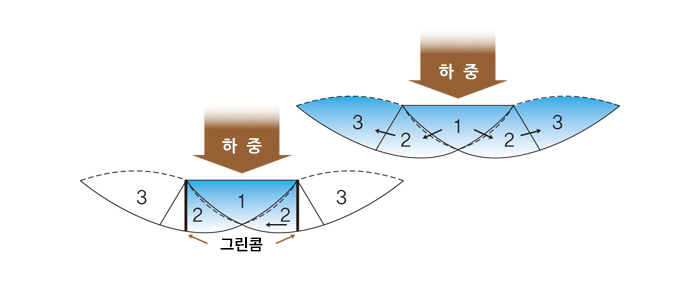
Without reinforcement, when load is applied in Zone 1 as shown,
soil wedge 1 pushes soil wedge 2, causing failure.
Reinforcing with Greencomb restrains the displacement of soil in Zone 2,
preventing failure and increasing the load-bearing capacity.

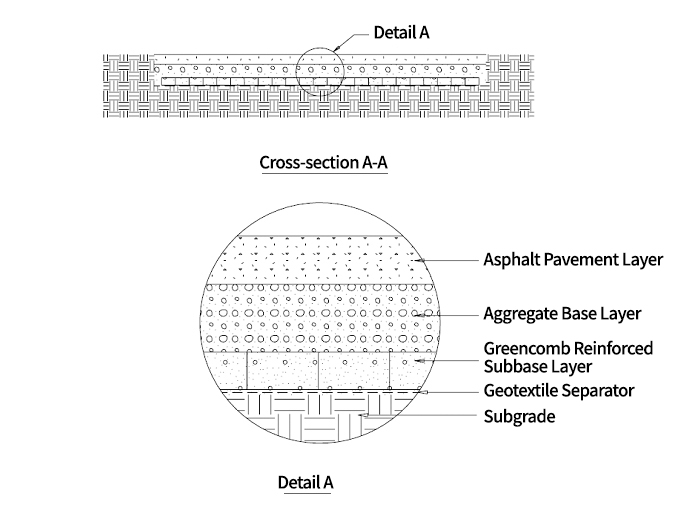

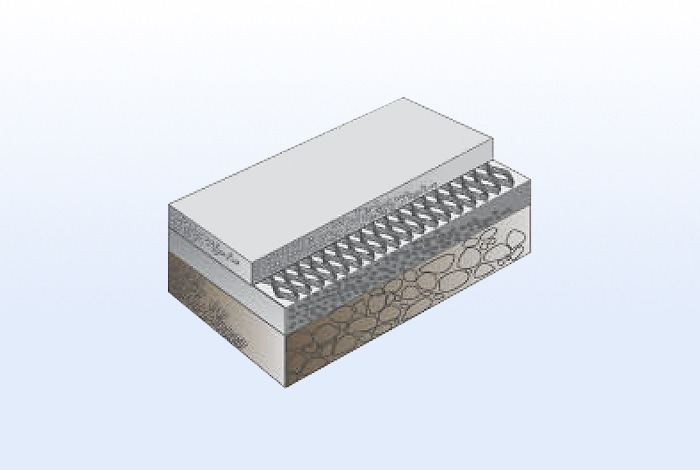
Reinforcement of base and sub-base for paved and unpaved roads,
temporary roads on weak ground, yard and parking lot sub-bases, and railway subgrade reinforcement.
Greencomb restrains displacement of infill material, ensuring structural stability
and serving as a reinforcement layer for riverbanks and bed protection structures.
The Greencomb reinforcement layer reduces hydraulic forces and, through contact pressure
with the soil, prevents piping and erosion, contributing to stable river structure maintenance.
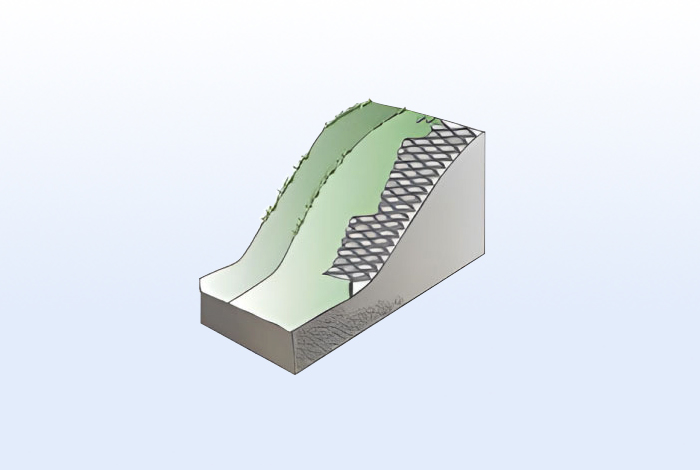
When used with vegetation mats, it forms a green slope protection layer
that enhances resistance against erosion caused by water flow.
Applicable to steep slopes with concrete or aggregate covering, Greencomb acts as formwork and
expansion joint, providing a flexible reinforcement layer that accommodates ground movement and controls cracking.
When plants grow within Greencomb infill, roots interlock
with the porous structure, creating an integrated, stable protective layer for the slope.
Applied in rivers or channels, Greencomb restrains infill displacement,
minimizing soil loss due to water flow and forming more natural banks when combined with plant roots.
Using vegetation mats alongside Greencomb reduces sediment loss
from heavy rain, forming an erosion-preventing layer and enhancing overall slope stability.


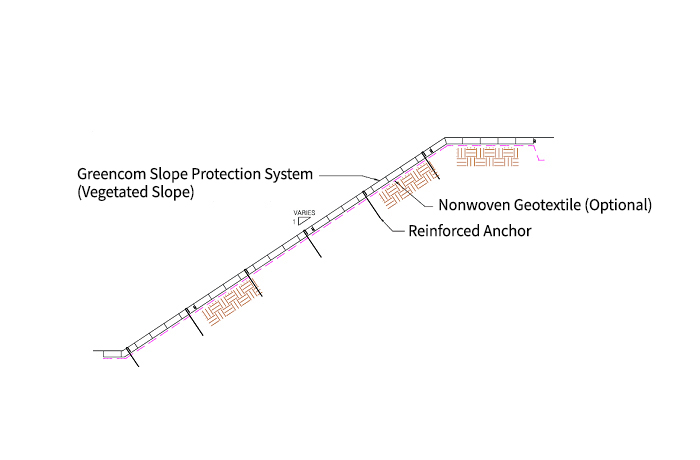
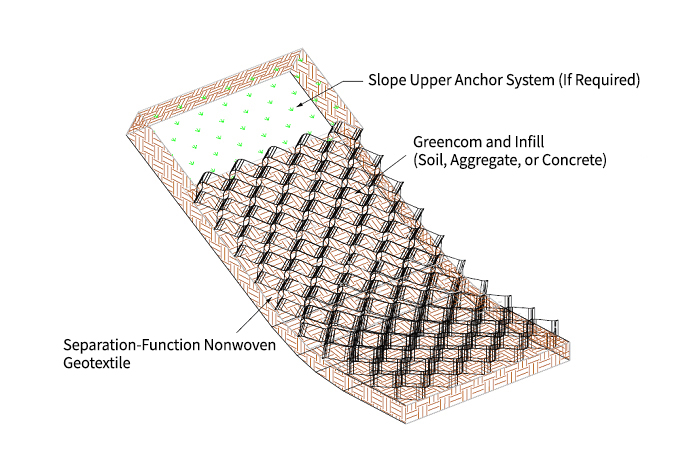
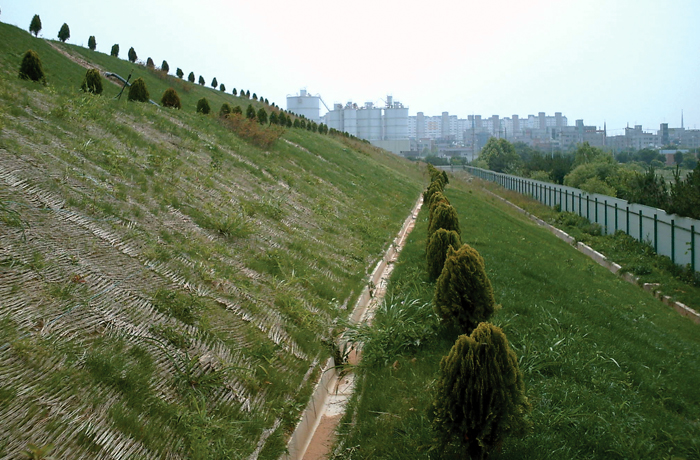
Vegetated embankment slope protection, levee greening
slope protection, riverbank protection, agricultural and irrigation channel slope protection


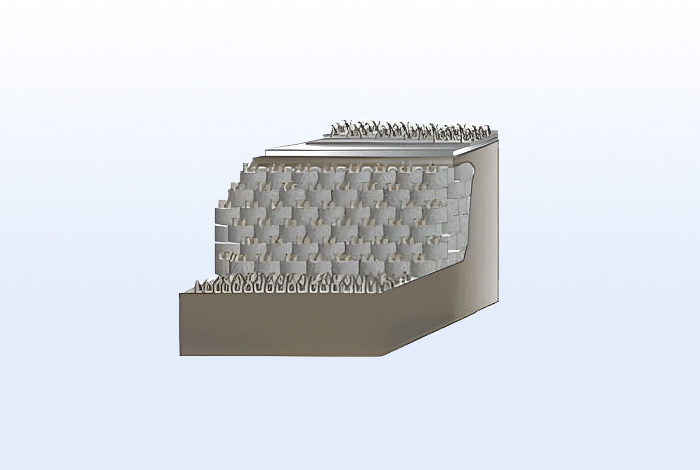
Greencomb forms a reinforcement layer through infill and compaction,
and by stacking these layers repeatedly, the desired height of the soil structure is achieved.
High friction between Greencomb layers enhances the stability of the overall structure.
Horizontal stress generated in the backfill soil is accommodated
by the Greencomb reinforcement layers, forming a solid reinforced soil structure.
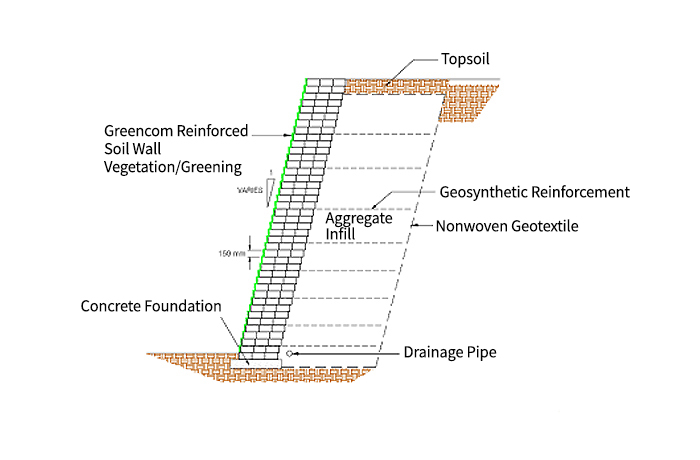
Vegetated MSE walls, vegetated reinforced slopes,
reinforced embankments, landslide slope restoration, collapsed levee restoration